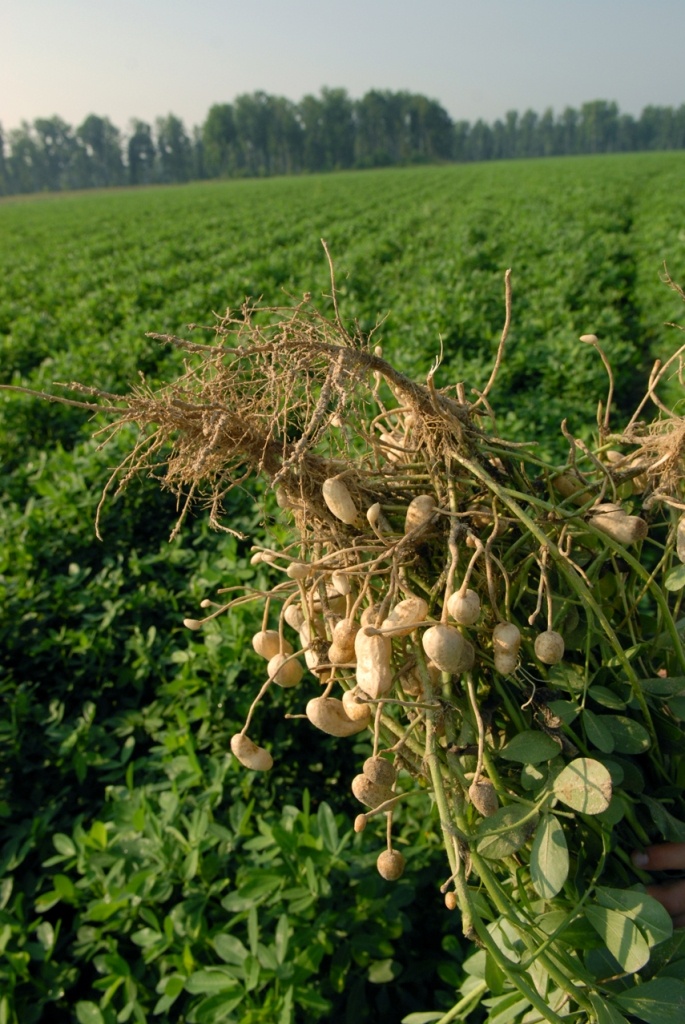
Agricultural development in Gujarat has reached a remarkable milestone as groundnut production soars to unprecedented levels. According to the first advance estimates for 2024-25, the groundnut crop (kharif) is projected at 103.60 lakh tons compared to 86.60 lakh tons in 2023-24 . This significant increase highlights the state’s growing agricultural prowess.
We can see Gujarat firmly establishing itself as the nation’s groundnut powerhouse, leading production with an impressive 52.25 lakh tons, followed by Rajasthan (21.27 lakh tons) and Madhya Pradesh (14.35 lakh tons) . Furthermore, Gujarat dominates in area coverage with 19.17 lakh hectares dedicated to groundnut cultivation . Despite this tremendous growth in india agricultural development, farmers face market challenges as groundnut prices have eased marginally by 1% to Rs.5,909 per quintal compared to Rs.5,963 in the previous week . Additionally, the role of agricultural development corporations remains crucial, with NAFED having procured 386,041.79 MT of groundnut under the Price Support Scheme at an MSP of Rs. 6,783 per quintal as of December 23, 2024 . This situation offers valuable insights for international agricultural development strategies in similar agrarian economies.
What led Gujarat to a record 66 lakh ton groundnut yield?
Gujarat’s groundnut production has surged dramatically, with the state poised to produce a historic 66 lakh metric tons in 2025 [1]. This remarkable achievement stems from several interconnected factors that have transformed the state’s agricultural landscape.
Improved rainfall and irrigation infrastructure
Favorable rainfall patterns coupled with enhanced irrigation systems have played a pivotal role in boosting yields. Studies reveal a strong positive relationship between groundnut production and irrigation, with of production variance irrigation levels accounting for approximately 50.3%[2]. Notably, Gujarat has steadily increased its irrigation coverage from merely 2.23% in the 1950s to 33.12% in recent years [3].
The implementation of modern irrigation techniques has been particularly effective. Research shows drip irrigation resulted in a substantial 79% increase in groundnut yield while simultaneously reducing water consumption by 36% [2]. Consequently, the average yield per hectare in Gujarat increased to 2,210 kg compared to 2,025 kg the previous year—a 9.13% improvement [4].
Expansion in sown area across key districts
The area under groundnut cultivation has expanded significantly across Gujarat. From 15.94 lakh hectares in 2018-19, the area has grown by 25% to reach 22 lakh hectares in 2025 [1]. This expansion is primarily concentrated in Saurashtra region, often referred to as the “peanut hub.”
Key contributing districts include:
- Dwarka (5.43 lakh MT)
- Rajkot (5.36 lakh MT)
- Amreli (increased from 1.511 lakh hectares to 2.07 lakh hectares) [5]
Farmers have increasingly shifted from cotton to groundnut cultivation due to issues with pink bollworm infestation in cotton crops and the attractive economics of groundnut farming [5]. Groundnut’s shorter 100-120 day growing cycle (versus 180 days for cotton) also allows farmers to plant a second crop during the winter season [5].
Support from agricultural development corporations
Agricultural development initiatives have significantly influenced productivity improvements. Programs like UPL’s ProNutiva have helped farmers increase yields by as much as 35% [6]. This initiative, implemented across 12,000 acres with 4,000 farmers in 2021, has now benefited over 75,000 farmers covering 2.5 lakh acres [6].
Farmers now primarily cultivate research-based high-yield varieties developed by state agricultural universities and the Indian Peanut Research Institute, including Gujarat Groundnut-20, 32, 39, 23, and Girnar-4 [1]. These specialized varieties, along with integrated agricultural services like soil testing and crop advisory, have contributed to groundnut yield enhancements throughout the state.
How does Gujarat’s output reshape India’s groundnut landscape?
The groundnut cultivation landscape in India has been fundamentally altered by Gujarat’s unprecedented productivity. With its monumental output, the state has become the unrivaled leader in the country’s groundnut sector.
Gujarat’s 50%+ share in national production
Gujarat’s dominance in India’s groundnut production is undeniable, contributing . In fact, the state’s share has grown from 39% in 2019-20 to nearly 55% in the current season. This remarkable increase means a single state now controls more than half of India’s entire groundnut output. Moreover, the state’s production efficiency outpaces the national average yield of 1,421 kg/hectare, with Gujarat farmers achieving . This productivity gap of 55.5% underscores the state’s agricultural superiority in this crop.over 50% to the national total2,210 kg/hectare
Shift in production dynamics among states
The rise of Gujarat has reshaped interstate production dynamics across India. Although Rajasthan maintains its position as the second-largest producer with 21.27 lakh tons, its relative contribution has declined as Gujarat expanded its lead. In contrast, Tamil Nadu has experienced a substantial drop in production, falling from its traditional third position. Concurrently, Madhya Pradesh has emerged as a significant player, now ranking third with 14.35 lakh tons. This realignment reflects a geographical shift in production centers toward western India, where climatic conditions and agricultural practices increasingly favor groundnut cultivation.
Implications for India agricultural development
The concentration of groundnut production in Gujarat presents both opportunities and challenges for India’s agricultural development strategy. On one hand, the state’s success provides a valuable model for agricultural development corporations seeking to replicate similar results elsewhere. Conversely, this concentration creates vulnerability in the national supply chain, as regional crop failures could disproportionately impact overall production. From a policy perspective, the emergence of regional specialization suggests the need for tailored approaches to agricultural development rather than one-size-fits-all national programs. Eventually, balancing regional strengths while encouraging diversified production bases will be crucial for sustainable agricultural growth throughout India.
Why are farmers still struggling despite bumper harvest?

Image Source: NewsClick
Despite Gujarat’s groundnut bounty, farmers face a troubling economic paradox. The record harvest has unfortunately created significant challenges for producers across the state.
Market prices fall below MSP
Primarily, market prices have declined beneath the government-set Minimum Support Price (MSP). In Gondal APMC, Gujarat’s largest wholesale groundnut market, modal prices fell to around compared to the MSP of ₹5,500 ₹5,250 per quintal[7]. Similarly, farmers in other regions report receiving between ₹1,140 and ₹1,350 per 20 kg, well below the MSP of ₹1,356 [8]. This price collapse occurs precisely when the state anticipates its highest-ever production.
Slow procurement under Price Support Scheme
The Price Support Scheme (PSS), designed to protect farmers when prices fall during peak harvesting periods [9], has been ineffective. Procurement operations have been hampered by financial constraints, with NAFED facing debt issues that affect its ability to purchase crops promptly [10]. Subsequently, the government extended procurement deadlines in several states—24 days in Maharashtra and 15 days in Telangana [11]—yet implementation remains inadequate.
Mismatch between supply and demand
Weak demand fundamentally undermines prices. Several factors contribute to this imbalance: quality issues from irregular rainfall, reduced demand for groundnut oil, and limited international competitiveness [7]. Historically, Chinese imports and purchases from Andhra Pradesh traders boosted prices, but both sources have diminished substantially [7]. Nevertheless, the government plans to purchase approximately at MSP rates 9.98 lakh metric tons[8], highlighting ongoing efforts to address these india agricultural development challenges.
What does this mean for future agricultural policy?
Gujarat’s groundnut success story highlights critical policy gaps in the national agricultural framework. Beyond production achievements, structural reforms are essential for long-term sustainability.
Need for faster procurement mechanisms
Supply-side bottlenecks hinder effective crop purchasing, requiring “mission mode” attention from policymakers [12]. Currently, the government plans to procure of 14 agricultural commodities this kharif season approximately 828 lakh metric tons[12]. To address these challenges, experts recommend mandatory WDRA registration for warehouses built under government schemes [12]. Henceforth, declaring storage infrastructure as “deemed sub-market yards” under state APMC acts could reduce logistics costs substantially [12].
Potential reforms in MSP implementation
The Shanta Kumar Committee reveals successfully sell produce at MSP rates only 6% of farmers[13]. This disparity necessitates fundamental rethinking of price support mechanisms. Interestingly, financial departments suggested implementing a five-year MSP policy for oilseeds—though ultimately rejected by the Agriculture Ministry [12]. As an alternative, some propose direct compensation to farmers selling below MSP, estimated to cost between ₹30,000-50,000 crores versus ₹7.5 lakh crores for complete procurement [14].
Lessons for international agricultural development
Cash flow constraints persistently prevent smallholder farmers from purchasing necessary inputs [1]. Throughout developing nations, underdeveloped value chains create barriers between producers and markets [1]. Moving forward, collectivization through Farmer Producer Companies offers promising solutions by enabling bulk input purchases, collective bargaining, and establishing village-level processing units [15].
Conclusion
Gujarat’s remarkable achievement of 66 lakh ton groundnut production stands as a testament to the state’s agricultural prowess. The perfect combination of improved irrigation infrastructure, expanded cultivation area, and support from agricultural development corporations has undoubtedly propelled this historic harvest. Nevertheless, the paradox remains that despite this bounty, farmers continue to struggle with prices falling below MSP and inadequate procurement mechanisms.
The shifting production dynamics across India reflect a broader transformation, with Gujarat now controlling over 50% of national groundnut output. This concentration certainly creates both opportunities and vulnerabilities for India’s agricultural sector. Farmers, meanwhile, face the harsh reality that increased production does not automatically translate to economic prosperity.
Looking ahead, policymakers must address several critical challenges. First, the implementation of faster procurement mechanisms becomes essential to ensure farmers receive fair compensation. Additionally, fundamental reforms in MSP implementation could help bridge the gap between theoretical support prices and market realities. We believe these lessons extend beyond India’s borders, offering valuable insights for agricultural development strategies worldwide.
The Gujarat groundnut story ultimately reminds us that agricultural policy must balance production goals with economic sustainability for farmers. Though record harvests grab headlines, the true measure of success lies in the financial stability of those who till the soil. Accordingly, future policies should focus equally on productivity and profitability. Therefore, we invite you to subscribe to our newsletter for more updates on how this agricultural saga unfolds in the coming seasons.
Key Takeaways
Gujarat’s groundnut success demonstrates how agricultural infrastructure and policy reforms can drive record production while revealing critical gaps in farmer support systems.
• Gujarat achieves historic 66 lakh ton groundnut harvest through improved irrigation, expanded cultivation area, and agricultural development support programs.
• The state now controls over 50% of India’s groundnut production, fundamentally reshaping national agricultural dynamics and regional specialization patterns.
• Despite record yields, farmers struggle with market prices falling below MSP due to weak demand and slow government procurement mechanisms.
• Only 6% of farmers successfully sell at MSP rates, highlighting urgent need for procurement reforms and direct compensation mechanisms.
• Agricultural policy must balance production goals with economic sustainability, ensuring increased yields translate to farmer profitability and financial stability.
This case study offers valuable lessons for international agricultural development, showing that production success requires equally robust market support systems to truly benefit farmers.
FAQs
Q1. What factors contributed to Gujarat’s record groundnut production? Improved rainfall, enhanced irrigation infrastructure, expansion of cultivated area, and support from agricultural development corporations all played crucial roles in boosting Gujarat’s groundnut yield to record levels.
Q2. How has Gujarat’s groundnut production affected India’s agricultural landscape? Gujarat now contributes over 50% of India’s total groundnut production, reshaping the national agricultural dynamics and leading to a geographical shift in production centers towards western India.
Q3. Why are farmers struggling despite the bumper groundnut harvest? Farmers are facing challenges due to market prices falling below the Minimum Support Price (MSP), slow procurement under the Price Support Scheme, and a mismatch between supply and demand in the groundnut market.
Q4. What changes are needed in agricultural policy to address farmers’ challenges? Future agricultural policies should focus on implementing faster procurement mechanisms, reforming MSP implementation, and balancing production goals with economic sustainability for farmers.
Q5. How does Gujarat’s groundnut production compare to other states in India? Gujarat leads groundnut production in India, followed by Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh. The state’s productivity significantly outpaces the national average yield, with Gujarat farmers achieving 2,210 kg/hectare compared to the national average of 1,421 kg/hectare.
References
[1] – https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/19439342.2024.2319657
[3] – https://malque.pub/ojs/index.php/msj/article/download/8163/4139/58074
[8] – https://english.gujaratsamachar.com/news/gujarat/farmers-in-gujarat-paid-below-msp-for-groundnut
[9] – https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2135955
[13] – https://tarunias.com/exams/upsc/minimum-support-price-msp-upsc/
[15] –https://www.ceeindia.org/pdf_files/Groundnut%20_Note.pdf
author: Shree Shubham Exim
date Published: 2025-10-03
Gujarat groundnut production, oilseed export, MSP groundnut, agriculture India, snack industry supply